ECS 170: Introduction to AI
Instructor: Rao Vemuri
Homework Assignment # 1: Solution
Due: 21 January 2003
(100 points)
This problem is based on Problem Formulation
1. (20 points). The Cannibals-Missionaries Problem. Consider the problem of three cannibals and three edible missionaries seeking to cross a river in a boat that can hold at most two individuals and can be navigated by one or any combination of two individuals. Under no circumstances can the missionaries be outnumbered by the cannibals, anywhere.
This problem has been solved in a
variety of ways. For our problem, let the ordered pair (m, c) denote the number
of cannibals and missionaries on the first bank.
(a) Give your version of a solution to this problem by writing a sequence of
state transitions. Use the above cited ordered pair as the state and an arrow
to indicate a state transition.
(b) This problem is simple to solve once you have the correct representation.
One way of doing this is to represent the
states as discrete points in a two-dimensional m-c plane. Using m as the
abscissa and c as the ordinate, plot ALL the possible states. All these states
are NOT admissible; i. e., some states are prohibited by the rules of the
problem. Identify the admissible states by solid circles (i. e., dots
completely filled) and inadmissible states by open circles.
(c) Now show on this diagram, every boat passage by a directed arrow. That is,
a transition, such as (3,3) --> (3,1) will be represented by a directed
arrow from (3,3) to (3,1). Show the complete solution by a sequence of directed
arrows.
Solution:
Let the ordered pair
(m,c) represent the number of cannibals and missionarieson the first (left)
bank.
Then the initial state is (3,3)
Goal State is (0, 0)
The state transitions
required for a solution are:
(3, 3) > (3, 1) >
((3, 2) > (3, 0) > (3, 1) > (1, 1) > (2, 2) > (0, 2) >
(0, 3) > (0, 1) > (0, 2) > (0,0)
Every
passage of the boat represents a state transition. On a sheet of paper draw the
x-axis and y-axis and mark the points (x,y) for x, y = 0, 1, 2,3. Then cross
off the points that are not admissible. Then using arrows link the traversal of
the boat. Look at the diagram and see if you can detect a pattern.
Note
that (1, 2), (1, 3) and 2, 3) states are prohibited. Any state where c > m
> 0 is not admissible. But c > m = 0 is admissible.
These problems are based on Search
Consider a road map such as the one shown in Figure.
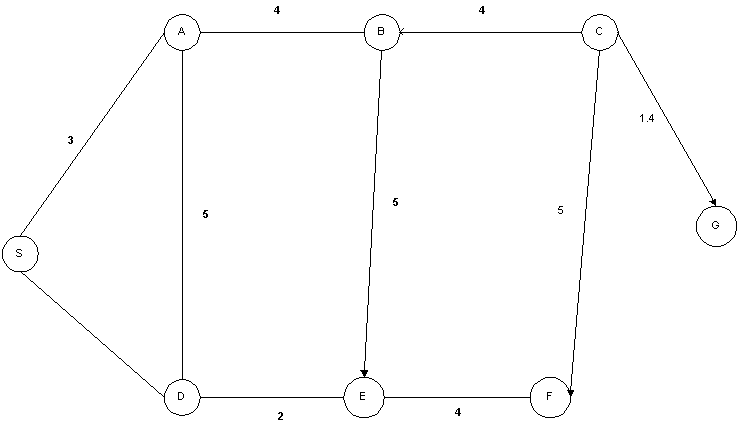
2. (10 points) Draw a tree of all loop-free paths that is equivalent to the net shown above. When a node has more than one child, arrange them in alphabetical order.
Solution: Draw a tree as follows. I hope my
notation is self explanatory. If I had more time, I would have drawn an actual
tree.
(S, (A, D) ) – That is S is the root node A is
the left child and D is the right child
(A, (B, D) ) – That is A is the parent node B is
the left child and D is the right child
(B, (C, E) ) –
(C, (F, G) ) – Here G is the goal node
(E, (D, F) )
(D, (E) )
(E, (B, F) )
etc etc.
2. (10 points) Show how DFS would search the net shown in the above figure
3. (10 points) Show how BFS would search the net shown in the above figure
4. (10 points) On page76 of the book, the authors said that they would not consider the case of negative path costs. Suppose that a negative lower bound c is placed on the cost of any given step (that is, negative costs are allowed, but they cannot go below a specified c). Does this allow uniform-cost search to avoid searching the whole tree? Explain in one or two sentences.
Negative costs are indicative of some error in
the formulation of the problem. However, the answer to the question is NO. the
algorithm still must explore every branch of the tree. Because it is possible
for you to encounter a sequence of negative costs or you may find yourself in a
loop and the accumulated negative cost can potentially exceed the bound.
5. (20 points) The GENERAL-SEARCH algorithm executes the following three
steps in the indicated order: goal test, generate, ordering function. It is a
shame to generate a node that is in fact a solution, but fail to recognize it
immediately because the ordering function fails to place it first in the queue.
(a) Write a version of GENERAL-SEARCH that tests each node as soon as it is
generated and stops immediately if it has found the goal.
(b) Show how GENERAL-SEARCH can be used unchanged to do this by giving it the
proper ordering function.
Solution: (a) This exercise illustrates the
flexibility of the search algorithm given in the book.
function
General-Search-New(problem, Queuing-FN) returns a solution, or
failure
nodes
ß
Make-Queue(MAKE-NODE(INITIAL STATE[problem]) )
loop
do
if nodes is empty then return failure
node
ß REMOVE-FRONT(nodes)
new-node
ß EXPAND(node,
OPERATORS[problem])
if
GOAL-TEST[problem] applied to the STATE of any of new-nodes succeeds then
return that node
nodes
ß QUEUING-FN-FRONT(nodes,
new-nodes)
end
(b) We could just call the original GENERAL-SEARCH with a queuing function that includes a call to the goal test function. If a node passes the goal test, it is placed at the very front of the queue; otherwise it is placed at the “normal” position.
6 (10 points) Suppose that we run a greedy algorithm with h (n) = - g(n). What sort of search does this greedy search emulate? Explain
Solution: Setting h (n) = - g(n) means
the best nodes will be those with the longest path. Preferring longest path
means DFS. If we set h (n) = g(n) then it would be BFS.
7. (10 points) Prove that IF the heuristic function h obeys the
triangle inequality, THEN the f-cost along any path in the search tree is
non-decreasing. (The triangle inequality says that the search cost from A to B
and B to C must not be less than the cost from A to C directly.)
Solution: Consider two nodes n and n’. Let ![]() is the cost of the shortest path from n to n’. Then the
triangle inequality says that
is the cost of the shortest path from n to n’. Then the
triangle inequality says that
![]()
Non-decreasing f-cost along a
path means that the f-cost of a successor is always equal to or greater than
that of the node itself.
![]() if
if ![]()
Because f = g + h, we can
rewrite the above as
![]() if
if ![]()
Our goal is to show that
this is implied by the triangle inequality. Adding g(n) to both sides of the
TE, we get
![]()
If n’ is a successor of n, then ![]() is equal to
is equal to ![]() . Therefore
. Therefore
![]()
QED
Department of Computer Science
University of California at Davis
Davis, CA 95616-8562
Page last modified on 1/10/2003