The "brain" of a computer is its central processing unit (CPU). It is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions in the program.
Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates fetching (from memory), decoding and execution of instructions by directing the coordinated operations of the ALU, registers and other components.
In this chapter, we cover the digital logic gates that allows the CPU to perform operations, the structure of the CPU, as well as introduce the different components that make a computer.
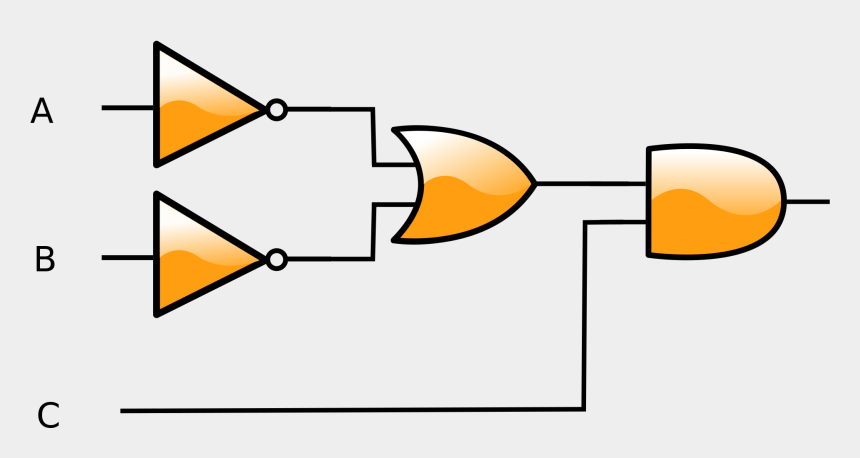
The building blocks for (¬(A∧B))∧C.
Lecture Notes
Further Reading
Handwritten Notes from class on 1/21: Inverter PDF document
Handwritten Notes from class on 1/23: Inverter / AND gate PDF document
Handwritten Notes from class on 1/26: OR gate; DeMorgan's laws PDF document
Cheat sheet on Gates: PDF document





