|
|
AIX008: Introduction to Data Science: Summer 2022
Supervised learning: k-Nearest Neighbour
The k-nearest neighbors algorithm (k-NN) is a non-parametric supervised learning method. It is used for classification and regression.
In both cases, the input consists of the k closest training examples in a data set. The output depends on whether k-NN is used for classification or regression:
- In k-NN classification, the output is a class membership. An object is classified by a plurality vote of its neighbors,
with the object being assigned to the class most common among its k nearest neighbors (k is a positive integer, typically small).
If k = 1, then the object is simply assigned to the class of that single nearest neighbor.
- In k-NN regression, the output is the property value for the object. This value is the average of the values of k nearest neighbors.
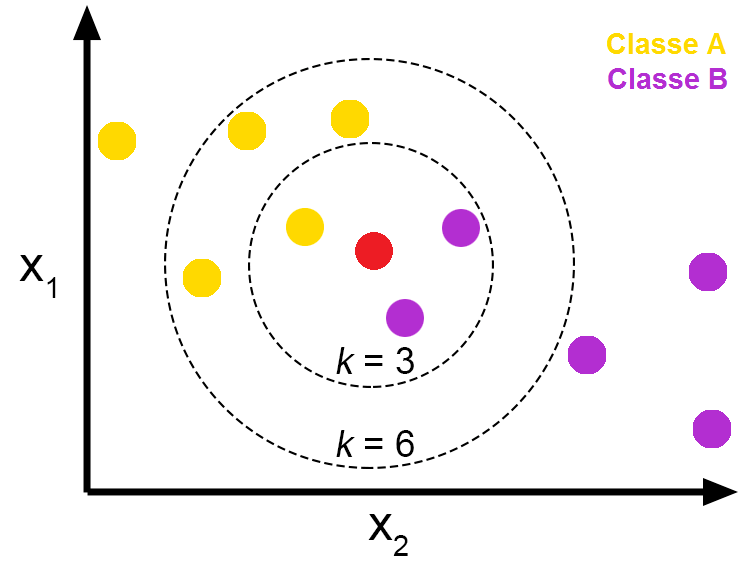
Example of the use of kNN for classification. if k=1, the test point (in read) is assigned to class B. If k=3, it is assigned to class A.
Lecture Notes
Further Reading
|





